Product analysis:
Ethylene glycol, also known as monoethylene glycol or MEG, is an odorless, colorless, flammable, hygroscopic liquid that is toxic in its high concentrations. It is the simplest combination of glycols and one of the most common organic compounds with the formula of C2H6O2. It can be gained from the reaction of ethylene oxide and water. Not only does it have low volatility and low viscosity, but it is also completely miscible with water and many other organic liquids like alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and esters. This sweet-taste chemical can be mixed with water in any proportion. MEG is commonly used as a raw material for antifreeze fluids. Furthermore, the high boiling point of ethylene glycol and its strong affinity for water make it an ideal dehydrating agent for natural gas production.
- Wide liquid range
This feature means that MEG can stay in the liquid state across a wide range of temperatures at standard atmosphere pressure. It is due to its high boiling point of 197.3°C (387.1°F) and low freezing point of -12.9°C (8.8°F). It is versatile and can be used across different environmental conditions and industries.
- Low volatility
This feature is related to the ability of MEG to resist evaporation under a normal atmosphere. It reduces the risk of creating flammable or explosive vapors, making MEG safer to handle and store. In addition, it means less product waste during storage, transportation, and use, leading to better efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Low viscosity
That means MEG can flow easily, especially at typical operating temperatures. So it can mix with other substances effortlessly, leading to better mass transfer and reaction rates.
- High miscibility
MEG can easily blend with water and many organic solvents to form a homogeneous solution. It can mix with these compounds at various concentrations without separating into distinct layers. MEG’s high miscibility allows it to be used in a wide range of applications where mixing with other substances is crucial.
- Highly hygroscopic
MEG has a strong desire for water molecules and can absorb moisture from its surroundings. It can come into contact with various environments or substances to remove water effectively. This property is crucial in many industrial processes where water removal or control is necessary.
There is a strong global need for Monoethylene Glycol as it is a vital ingredient. Due to the reactivity of the hydroxyl group and its high degree of solubility, ethylene glycol offers a wide range of applications. The ability to mix readily and form stable solutions enhances MEG’s versatility, efficiency, and effectiveness in numerous processes.
- Polyester production
MEG is a key component in synthesizing polyester fibers, films, and resins. It is used to produce polyethylene terephthalate (PET) for plastic bottles and packaging. Polyester fibers, threads, films, and polyester resins are produced from the reaction between MEG with dibasic acids and their esters and it is used in the synthesis of PET.
- Resin production
It is used in synthesizing unsaturated polyester resins, alkyd resins, rosin esters, and polyurethane resins. It acts as a coalescence and anti-freezing agent in emulsified resins. It is used together with adipic acid and other glycols, and rubber with a high chemical and abrasion resistance. Resins produced from oleic acid and MEG, known as alkyd resins, are used frequently in the industry of paints and varnishes. It also can be used as a wetting and plasticizing agent in the production of cellophane, glues and adhesives, textiles, printing ink, leather, cosmetics, paper, and pharmaceutical products.
- Antifreeze and coolants
Because of its low freezing point, it can decrease the freezing point of water in automotive antifreeze. So, it is used in aircraft de-icing and anti-icing agents. Plus, it is used in industrial refrigeration circuits and internal combustion engine coolant systems to raise the boiling point and reduce the freezing point of the solution used. It can also be utilized in the formulation of printing ink, in the treatment of gases, in the formulation of fire-resistant hydraulic fluids, cutting oils, surface polishers, agrochemicals, extraction of solvents, manufacture of pigmented pastes and putty for walls, and in the synthesis of explosives.
- Textile industry
MEG is a component in polyester fiber synthesis for sports and casual wear. It is used as a wetting and plasticizing agent in textile production. Polyester fibers have high strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and wrinkling.
- Packaging materials
MEG is a key ingredient in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) production for making bottles, containers, films, and trays. PET has excellent transparency, mechanical strength, and recyclability.
- Chemical intermediate
It serves as a raw material, solvent, plasticizer, humectant, and intermediate in various chemical syntheses. MEG is also used to produce unsaturated polyester resins, polyurethane systems, detergents, morpholine, and other organic compounds.
- Natural gas processing
MEG acts as a dehydration agent in natural gas pipelines. It can inhibit the formation of natural gas clathrates.
- Automotive industry
It is used as a lubricant for moving parts in cooling systems and as an additive for electrolytic polishing belts, besides antifreeze.
- Aviation industry
It can be applied as a de-icing and anti-icing agent for aircraft. It leads to preventing ice formation on the wings, fuselage, and other parts of the aircraft.
Monoethylene Glycol (MEG) can be delivered in various packaging options, including drums, Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBC), and tanks, depending on the required quantity. Petrobon supplies MEG to different cities across several countries, making the logistics process and costs vary based on location. For detailed information on transportation options and tailored solutions for your needs, contact Petrobon’s professional team. They can provide guidance based on your location and specific requirements to ensure smooth and cost-effective delivery.
It is a fact that global oil prices are variable. That means there is no stable and specific price for MEG. Please, contact us to inquire about the daily prices. You can also find the price changes of this material in the chart in this section.
MEG is classified as a harmful chemical especially if swallowed. It can irritate your eyes and skin. However, inhaling the vapor of Monoethylene Glycol is not hazardous. Plus, MEG vapors are nonirritating to the eyes and throat.
Ingestion of Monoethylene Glycol causes stupor or coma and sometimes leads to fatal kidney injury. It can be toxic to the kidneys, liver, and central nervous system (CNS). Repeated exposure to a highly toxic material can produce general deterioration of health by an accumulation in one or many human organs.
This substance can change the genetic material in mammal body cells, which could be harmful, but it doesn’t have the same effect on simpler organisms like bacteria or yeast. It can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate it and groundwater.
Monoethylene glycol can be stored in stainless Steel, Aluminum, or lined drums, tank cars, or tank trucks. MEG has a specific gravity of 1.115 and a flash point of 110 °C. Store Mono Ethylene Glycol in the original container protected from direct sunlight in a dry, cool, and well-ventilated area, away from incompatible materials and food and drink. Keep MEG away from strong Oxidants, strong Bases, and strong Acids. Keep the container of Mono Ethylene Glycol tightly closed and sealed until ready for use.
The simplest and the first way to recognize MEG is by considering its physical features. At normal temperature, it is a clear, colorless, odorless liquid with a viscous touch. If you add it to water it can easily mix without making layers. For laboratory checking, you can test its boiling or freezing point and you can also measure its density which requires a precise scale and volumetric equipment.
Gas chromatography (GC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) are some more complex analytical techniques used in research and industrial settings.
Generally, MEG can be produced through traditional methods and bio-based processes. The traditional method relies on fossil fuel feedstocks and is energy-intensive while bio-based approaches and processes using renewable energy sources are more sustainable. The choice of production method often depends on factors like raw material availability, energy costs, environmental regulations, and market demands in different regions.
Production of MEG initiates with the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide (EO), which itself is obtained via ethylene oxidation. In this process, ethylene oxide reacts with raw materials and, according to the desired chemical equation, ethylene glycol is produced. In this process, acids and bases are used as catalysts, and these materials can even be produced at high temperatures in acidic or neutral pH levels.
The highest amount of ethylene glycol can be obtained with acidic or neutral pH with an excess amount of water. Approximately 90% of ethylene glycol can be obtained under these conditions. The prominent by-products of this process are trimethylene glycol, tetramethylene glycol, and diethylene glycol oligomers.
SUPPLIERS
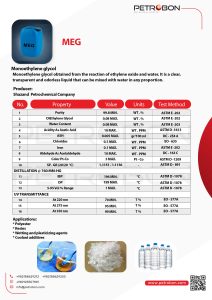
Shazand CO. Monoethylene glycol (MEG)
The Monoethylene glycol is a Shazand Petrochemical product. You can see the technical specifications of MEG | Monoethylene glycol in the following datasheet.
Price inquiry
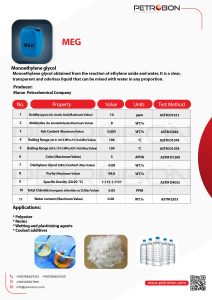
Marun CO. Monoethylene glycol (MEG)
The Monoethylene glycol is a Marun Petrochemical product. You can see the technical specifications of MEG | Monoethylene glycol in the following datasheet.
Price inquiry